Map layer that draws simple features as they are. Supported visual variables
are: fill (the fill color), col (the border color), size the point size,
shape the symbol shape, lwd (line width), lty (line type), fill_alpha (fill color alpha transparency)
and col_alpha (border color alpha transparency).
The visual variable arguments (e.g. col) can be specified with either a data
variable name (of the object specified in tm_shape()), or with a visual value
(for col, a color is expected). Multiple values can be specified: in that case
facets are created. These facets can be combined with other faceting data variables,
specified with tm_facets().
Usage
tm_sf(
fill = tm_const(),
fill.scale = tm_scale(),
fill.legend = tm_legend(),
fill.free = NA,
col = tm_const(),
col.scale = tm_scale(),
col.legend = tm_legend(),
col.free = NA,
size = tm_const(),
size.scale = tm_scale(),
size.legend = tm_legend(),
size.free = NA,
shape = tm_const(),
shape.scale = tm_scale(),
shape.legend = tm_legend(),
shape.free = NA,
lwd = tm_const(),
lwd.scale = tm_scale(),
lwd.legend = tm_legend(),
lwd.free = NA,
lty = tm_const(),
lty.scale = tm_scale(),
lty.legend = tm_legend(),
lty.free = NA,
fill_alpha = tm_const(),
fill_alpha.scale = tm_scale(),
fill_alpha.legend = tm_legend(),
fill_alpha.free = NA,
col_alpha = tm_const(),
col_alpha.scale = tm_scale(),
col_alpha.legend = tm_legend(),
col_alpha.free = NA,
linejoin = "round",
lineend = "round",
plot.order.list = list(polygons = tm_plot_order("AREA"), lines =
tm_plot_order("LENGTH"), points = tm_plot_order("size")),
options = opt_tm_sf(),
zindex = NA,
group = NA,
group.control = "check",
...
)
opt_tm_sf(
polygons.only = "yes",
lines.only = "yes",
points.only = "yes",
point.per = "feature",
points.icon.scale = 3,
points.just = NA,
points.grob.dim = c(width = 48, height = 48, render.width = 256, render.height = 256)
)Arguments
- fill, fill.scale, fill.legend, fill.free
Visual variable that determines the fill color. See details.
- col, col.scale, col.legend, col.free
Visual variable that determines the col color. See details.
- size, size.scale, size.legend, size.free
Visual variable that determines the size. See details.
- shape, shape.scale, shape.legend, shape.free
Visual variable that determines the shape. See details.
- lwd, lwd.scale, lwd.legend, lwd.free
Visual variable that determines the line width. See details.
- lty, lty.scale, lty.legend, lty.free
Visual variable that determines the line type. See details.
- fill_alpha, fill_alpha.scale, fill_alpha.legend, fill_alpha.free
Visual variable that determines the fill color alpha transparency See details.
- col_alpha, col_alpha.scale, col_alpha.legend, col_alpha.free
Visual variable that determines the border color alpha transparency. See details.
- linejoin, lineend
line join and line end. See gpar() for details.
- plot.order.list
Specification in which order the spatial features are drawn. This consists of a list of three elementary geometry types: for polygons, lines and, points. For each of these types, which are drawn in that order, a
tm_plot_order()is required.- options
options passed on to the corresponding
opt_<layer_function>function- zindex
Map layers are drawn on top of each other. The
zindexnumbers (one for each map layer) determines the stacking order. By default the map layers are drawn in the order they are called.- group
Name of the group to which this layer belongs. This is only relevant in view mode, where layer groups can be switched (see
group.control)- group.control
In view mode, the group control determines how layer groups can be switched on and off. Options:
"radio"for radio buttons (meaning only one group can be shown),"check"for check boxes (so multiple groups can be shown), and"none"for no control (the group cannot be (de)selected).- ...
passed on to
tm_polygons(),tm_lines(), andtm_dots()- polygons.only
should only polygon geometries of the shape object (defined in
tm_shape()) be plotted? By default"ifany", which meansTRUEin case a geometry collection is specified.- lines.only
should only line geometries of the shape object (defined in
tm_shape()) be plotted, or also other geometry types (like polygons)? By default"ifany", which meansTRUEin case a geometry collection is specified.- points.only
should only point geometries of the shape object (defined in
tm_shape()) be plotted? By default"ifany", which meansTRUEin case a geometry collection is specified.- point.per
specification of how spatial points are mapped when the geometry is a multi line or a multi polygon. One of
"feature","segment"or"largest". The first generates a spatial point for every feature, the second for every segment (i.e. subfeature), the third only for the largest segment (subfeature). Note that the last two options can be significant slower.- points.icon.scale
scaling number that determines how large the icons (or grobs) are in plot mode in comparison to proportional symbols (such as bubbles). For view mode, use the argument
grob.dim- points.just
justification of the points relative to the point coordinates. Either one of the following values:
"left","right","center","bottom", and"top", or a vector of two values where first value specifies horizontal and the second value vertical justification. Besides the mentioned values, also numeric values between 0 and 1 can be used. 0 means left justification for the first value and bottom justification for the second value. Note that in view mode, only one value is used.- points.grob.dim
vector of four values that determine how grob objects (see details) are shown in view mode. The first and second value are the width and height of the displayed icon. The third and fourth value are the width and height of the rendered png image that is used for the icon. Generally, the third and fourth value should be large enough to render a ggplot2 graphic successfully. Only needed for the view mode.
Details
The .scale arguments determine the used scale to map the data values to visual
variable values. These can be specified with one of the available tm_scale_() functions.
The default scale that is used is specified by the tmap option scales.var.
The .legend arguments determine the used legend, specified with tm_legend().
The default legend and its settings are determined by the tmap options legend..
The .free arguments determine whether scales are applied freely across facets,
or shared. A logical value is required. They can also be specified with a
vector of three logical values; these determine whether scales are applied freely
per facet dimension. This is only useful when facets are applied (see tm_facets()).
There are maximally three facet dimensions: rows, columns, and pages. This only applies
for a facet grid (tm_facets_grid()). For instance, col.free = c(TRUE, FALSE, FALSE) means
that for the visual variable col, each row of facets will have its own scale,
and therefore its own legend. For facet wraps and stacks (tm_facets_wrap() and
tm_facets_stack()) there is only one facet dimension, so the .free argument requires
only one logical value.
Examples
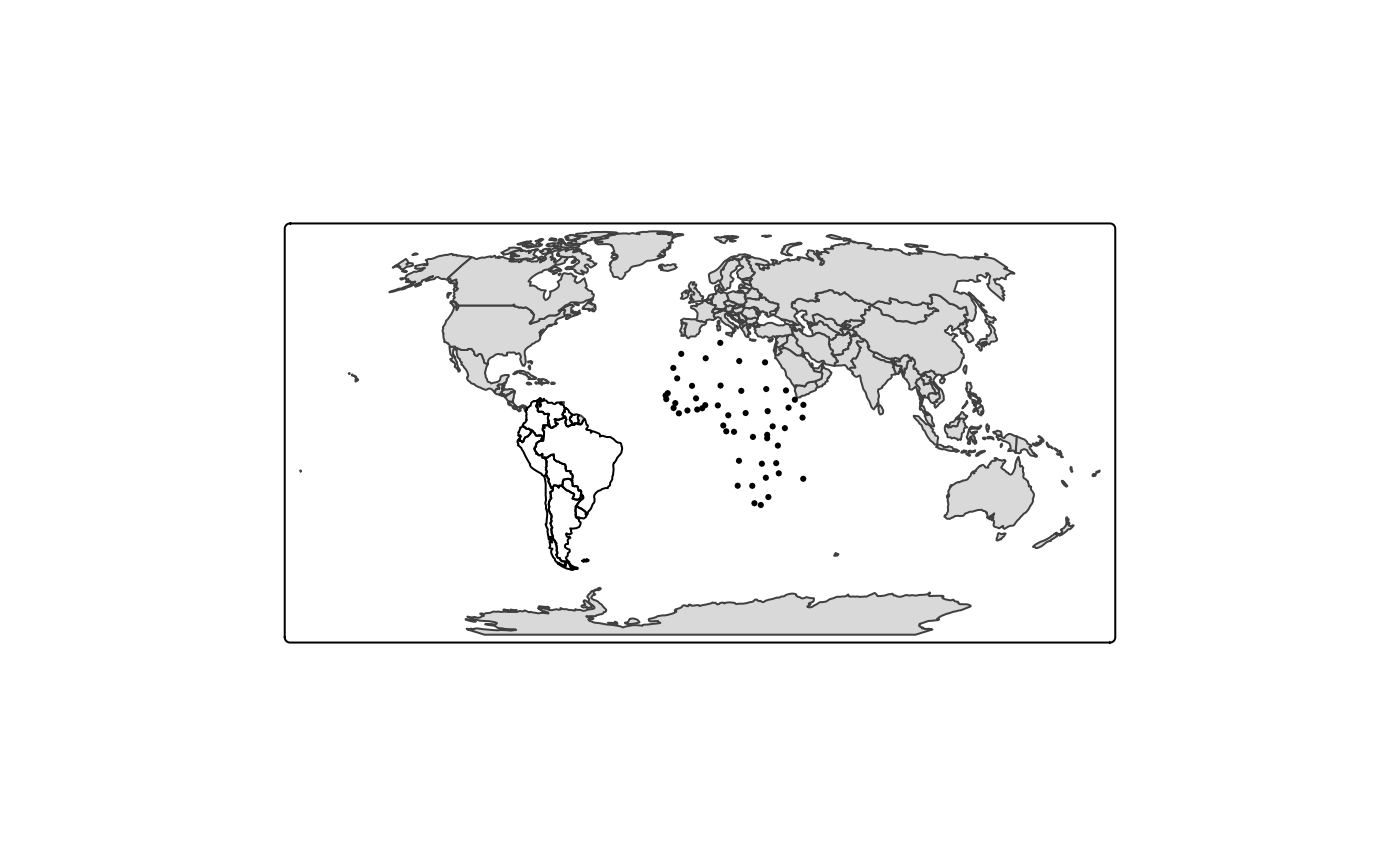
data(World)
World$geometry[World$continent == "Africa"] <-
sf::st_centroid(World$geometry[World$continent == "Africa"])
World$geometry[World$continent == "South America"] <-
sf::st_cast(World$geometry[World$continent == "South America"],
"MULTILINESTRING", group_or_split = FALSE)
tm_shape(World, crs = "+proj=robin") +
tm_sf()