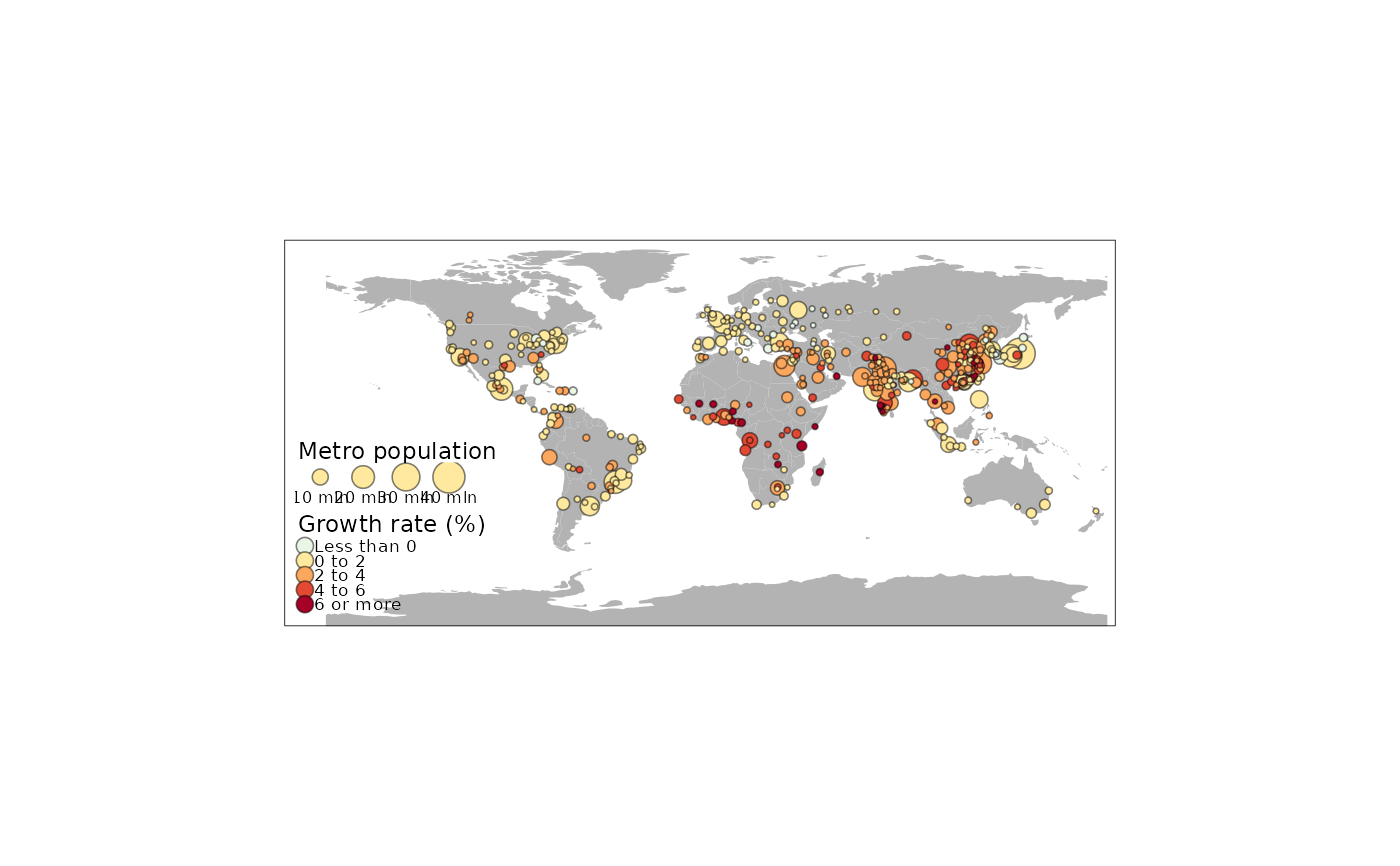
Map layer that draws symbols Supported visual variables are:
fill (the fill color), col (the border color), size the symbol size,
shape the symbol shape, lwd (line width), lty (line type), fill_alpha
(fill color alpha transparency) and col_alpha (border color alpha transparency).
Usage
tm_symbols(
size = tm_const(),
size.scale = tm_scale(),
size.legend = tm_legend(),
size.chart = tm_chart_none(),
size.free = NA,
fill = tm_const(),
fill.scale = tm_scale(),
fill.legend = tm_legend(),
fill.chart = tm_chart_none(),
fill.free = NA,
col = tm_const(),
col.scale = tm_scale(),
col.legend = tm_legend(),
col.chart = tm_chart_none(),
col.free = NA,
shape = tm_const(),
shape.scale = tm_scale(),
shape.legend = tm_legend(),
shape.chart = tm_chart_none(),
shape.free = NA,
lwd = tm_const(),
lwd.scale = tm_scale(),
lwd.legend = tm_legend(),
lwd.chart = tm_chart_none(),
lwd.free = NA,
lty = tm_const(),
lty.scale = tm_scale(),
lty.legend = tm_legend(),
lty.chart = tm_chart_none(),
lty.free = NA,
fill_alpha = tm_const(),
fill_alpha.scale = tm_scale(),
fill_alpha.legend = tm_legend(),
fill_alpha.chart = tm_chart_none(),
fill_alpha.free = NA,
col_alpha = tm_const(),
col_alpha.scale = tm_scale(),
col_alpha.legend = tm_legend(),
col_alpha.chart = tm_chart_none(),
col_alpha.free = NA,
plot.order = tm_plot_order("size"),
zindex = NA,
group = NA,
group.control = "check",
popup.vars = NA,
popup.format = tm_label_format(),
hover = NA,
id = "",
options = opt_tm_symbols(),
...
)
tm_dots(
fill = tm_const(),
fill.scale = tm_scale(),
fill.legend = tm_legend(),
fill.free = NA,
size = tm_const(),
size.scale = tm_scale(),
size.legend = tm_legend(),
size.free = NA,
lwd = tm_const(),
lwd.scale = tm_scale(),
lwd.legend = tm_legend(),
lwd.free = NA,
lty = tm_const(),
lty.scale = tm_scale(),
lty.legend = tm_legend(),
lty.free = NA,
fill_alpha = tm_const(),
fill_alpha.scale = tm_scale(),
fill_alpha.legend = tm_legend(),
fill_alpha.free = NA,
plot.order = tm_plot_order("DATA"),
zindex = NA,
group = NA,
group.control = "check",
options = opt_tm_dots(),
...
)
tm_bubbles(
size = tm_const(),
size.scale = tm_scale(),
size.legend = tm_legend(),
size.free = NA,
fill = tm_const(),
fill.scale = tm_scale(),
fill.legend = tm_legend(),
fill.free = NA,
col = tm_const(),
col.scale = tm_scale(),
col.legend = tm_legend(),
col.free = NA,
lwd = tm_const(),
lwd.scale = tm_scale(),
lwd.legend = tm_legend(),
lwd.free = NA,
lty = tm_const(),
lty.scale = tm_scale(),
lty.legend = tm_legend(),
lty.free = NA,
fill_alpha = tm_const(),
fill_alpha.scale = tm_scale(),
fill_alpha.legend = tm_legend(),
fill_alpha.free = NA,
col_alpha = tm_const(),
col_alpha.scale = tm_scale(),
col_alpha.legend = tm_legend(),
col_alpha.free = NA,
plot.order = tm_plot_order("size"),
zindex = NA,
group = NA,
group.control = "check",
options = opt_tm_bubbles(),
...
)
tm_squares(
size = tm_const(),
size.scale = tm_scale(),
size.legend = tm_legend(),
size.free = NA,
fill = tm_const(),
fill.scale = tm_scale(),
fill.legend = tm_legend(),
fill.free = NA,
col = tm_const(),
col.scale = tm_scale(),
col.legend = tm_legend(),
col.free = NA,
lwd = tm_const(),
lwd.scale = tm_scale(),
lwd.legend = tm_legend(),
lwd.free = NA,
lty = tm_const(),
lty.scale = tm_scale(),
lty.legend = tm_legend(),
lty.free = NA,
fill_alpha = tm_const(),
fill_alpha.scale = tm_scale(),
fill_alpha.legend = tm_legend(),
fill_alpha.free = NA,
col_alpha = tm_const(),
col_alpha.scale = tm_scale(),
col_alpha.legend = tm_legend(),
col_alpha.free = NA,
plot.order = tm_plot_order("size"),
zindex = NA,
group = NA,
group.control = "check",
options = opt_tm_squares(),
...
)
tm_markers(
text = tm_const(),
text.scale = tm_scale(),
text.legend = tm_legend(),
text.chart = tm_chart_none(),
text.free = NA,
size = tm_const(),
size.scale = tm_scale(),
size.legend = tm_legend(),
size.chart = tm_chart_none(),
size.free = NA,
col = tm_const(),
col.scale = tm_scale(),
col.legend = tm_legend(),
col.chart = tm_chart_none(),
col.free = NA,
col_alpha = tm_const(),
col_alpha.scale = tm_scale(),
col_alpha.legend = tm_legend(),
col_alpha.chart = tm_chart_none(),
col_alpha.free = NA,
fontface = tm_const(),
fontface.scale = tm_scale(),
fontface.legend = tm_legend(),
fontface.chart = tm_chart_none(),
fontface.free = NA,
fontfamily = "",
bgcol = tm_const(),
bgcol.scale = tm_scale(),
bgcol.legend = tm_legend(),
bgcol.chart = tm_chart_none(),
bgcol.free = NA,
bgcol_alpha = tm_const(),
bgcol_alpha.scale = tm_scale(),
bgcol_alpha.legend = tm_legend(),
bgcol_alpha.chart = tm_chart_none(),
bgcol_alpha.free = NA,
xmod = 0,
xmod.scale = tm_scale(),
xmod.legend = tm_legend_hide(),
xmod.chart = tm_chart_none(),
xmod.free = NA,
ymod = 0,
ymod.scale = tm_scale(),
ymod.legend = tm_legend_hide(),
ymod.chart = tm_chart_none(),
ymod.free = NA,
angle = 0,
angle.scale = tm_scale(),
angle.legend = tm_legend_hide(),
angle.chart = tm_chart_none(),
angle.free = NA,
plot.order = tm_plot_order("AREA", reverse = FALSE, na.order = "bottom"),
zindex = NA,
group = NA,
group.control = "check",
options = opt_tm_markers(),
...
)
opt_tm_markers(
markers_on_top_of_text = FALSE,
points_only = "ifany",
point_per = "feature",
on_surface = FALSE,
shadow = FALSE,
shadow.offset.x = 0.1,
shadow.offset.y = 0.1,
just = "center",
along_lines = TRUE,
bg.padding = 0.4,
clustering = TRUE,
point.label = TRUE,
point.label.gap = 0.4,
point.label.method = "SANN",
remove_overlap = FALSE,
dots.just = NA,
dots.icon.scale = 3,
dots.grob.dim = c(width = 48, height = 48, render.width = 256, render.height = 256)
)
opt_tm_symbols(
points_only = "ifany",
point_per = "feature",
on_surface = FALSE,
clustering = FALSE,
icon.scale = 3,
just = NA,
grob.dim = c(width = 48, height = 48, render.width = 256, render.height = 256)
)
opt_tm_dots(
points_only = "ifany",
point_per = "feature",
on_surface = FALSE,
clustering = FALSE,
icon.scale = 3,
just = NA,
grob.dim = c(width = 48, height = 48, render.width = 256, render.height = 256)
)
opt_tm_bubbles(
points_only = "ifany",
point_per = "feature",
on_surface = FALSE,
clustering = FALSE,
icon.scale = 3,
just = NA,
grob.dim = c(width = 48, height = 48, render.width = 256, render.height = 256)
)
opt_tm_squares(
points_only = "ifany",
point_per = "feature",
on_surface = FALSE,
clustering = FALSE,
icon.scale = 3,
just = NA,
grob.dim = c(width = 48, height = 48, render.width = 256, render.height = 256)
)Arguments
- size, size.scale, size.legend, size.chart, size.free
Visual variable that determines the size. See details.
- fill, fill.scale, fill.legend, fill.chart, fill.free
Visual variable that determines the fill color. See details.
- col, col.scale, col.legend, col.chart, col.free
Visual variable that determines the color. See details.
- shape, shape.scale, shape.legend, shape.chart, shape.free
Visual variable that determines the shape. See details.
- lwd, lwd.scale, lwd.legend, lwd.chart, lwd.free
Visual variable that determines the line width. See details.
- lty, lty.scale, lty.legend, lty.chart, lty.free
Visual variable that determines the line type. See details.
- fill_alpha, fill_alpha.scale, fill_alpha.legend, fill_alpha.chart, fill_alpha.free
Visual variable that determines the fill color transparency. See details. the fill color alpha transparency See details.
- col_alpha, col_alpha.scale, col_alpha.legend, col_alpha.chart, col_alpha.free
Visual variable that determines the color transparency. See details.
- plot.order
Specification in which order the spatial features are drawn. See
tm_plot_order()for details.- zindex
Map layers are drawn on top of each other. The
zindexnumbers (one for each map layer) determines the stacking order. By default the map layers are drawn in the order they are called.- group
Name of the group to which this layer belongs. This is only relevant in view mode, where layer groups can be switched (see
group.control)- group.control
In view mode, the group control determines how layer groups can be switched on and off. Options:
"radio"for radio buttons (meaning only one group can be shown),"check"for check boxes (so multiple groups can be shown), and"none"for no control (the group cannot be (de)selected).- popup.vars
names of data variables that are shown in the popups in
"view"mode. Set popup.vars toTRUEto show all variables in the shape object. Set popup.vars toFALSEto disable popups. Setpopup.varsto a character vector of variable names to those those variables in the popups. The default (NA) depends on whether visual variables (e.g.fill) are used. If so, only those are shown. If not all variables in the shape object are shown.- popup.format
list of formatting options for the popup values. Output of
tm_label_format(). Only applicable for numeric data variables. If one list of formatting options is provided, it is applied to all numeric variables ofpopup.vars. Also, a (named) list of lists can be provided. In that case, each list of formatting options is applied to the named variable.- hover
name of the data variable that specifies the hover labels (view mode only). Set to
FALSEto disable hover labels. By defaultFALSE, unlessidis specified. In that case, it is set toid,- id
name of the data variable that specifies the indices of the spatial features. Only used for
"view"mode.- options
options passed on to the corresponding
opt_<layer_function>function- ...
to catch deprecated arguments from version < 4.0
- text, text.scale, text.legend, text.chart, text.free
Visual variable that determines the text. See details.
- fontface, fontface.scale, fontface.legend, fontface.chart, fontface.free
Visual variable that determines the font face. See details.
- fontfamily
The font family. See gpar() for details.
- bgcol, bgcol.scale, bgcol.legend, bgcol.chart, bgcol.free
Visual variable that determines the background color. See Details.
- bgcol_alpha, bgcol_alpha.scale, bgcol_alpha.legend, bgcol_alpha.chart, bgcol_alpha.free
Visual variable that determines the background color transparency. See Details.
- xmod, xmod.scale, xmod.legend, xmod.chart, xmod.free
Transformation variable that determines the x offset. See details.
- ymod, ymod.scale, ymod.legend, ymod.chart, ymod.free
Transformation variable that determines the y offset. See details. the text. See details.
- angle, angle.scale, angle.legend, angle.chart, angle.free
Rotation angle
- markers_on_top_of_text
should markers be plot on top of the text (by default
FALSE)- points_only
should only point geometries of the shape object (defined in
tm_shape()) be plotted? By default"ifany", which meansTRUEin case a geometry collection is specified.- point_per
specification of how spatial points are mapped when the geometry is a multi line or a multi polygon. One of
"feature","segment"or"largest". The first generates a spatial point for every feature, the second for every segment (i.e. subfeature), the third only for the largest segment (subfeature). Note that the last two options can be significant slower.- on_surface
In case of polygons, centroids are computed. Should the points be on the surface? If
TRUE, which is slower than the defaultFALSE, centroids outside the surface are replaced with points computed withsf::st_point_on_surface().- shadow
Shadow behind the text. Logical.
- shadow.offset.x, shadow.offset.y
Shadow offset in line heights
- just
justification of the text relative to the point coordinates. Either one of the following values:
"left","right","center","bottom", and"top", or a vector of two values where first value specifies horizontal and the second value vertical justification. Besides the mentioned values, also numeric values between 0 and 1 can be used. 0 means left justification for the first value and bottom justification for the second value. Note that in view mode, only one value is used.- along_lines
logical that determines whether labels are rotated along the spatial lines. Only applicable if a spatial lines shape is used.
- bg.padding
The padding of the background in terms of line heights.
- clustering
in interactive modes (e.g.
"view"mode), should clustering be applied at lower zoom levels? EitherFALSE(default),TRUE, or a mode specific specification, e.g. for"view"modemarkerClusterOptions.- point.label
logical that determines whether the labels are placed automatically. By default
FALSEfortm_text, andTRUEfortm_labelsif the number of labels is less than 500 (otherwise it will be too slow).- point.label.gap
numeric that determines the gap between the point and label
- point.label.method
the optimization method, either
"SANN"for simulated annealing (the default) or"GA"for a genetic algorithm.- remove_overlap
logical that determines whether the overlapping labels are removed
- dots.just
justification of the text relative to the point coordinates. Either one of the following values:
"left","right","center","bottom", and"top", or a vector of two values where first value specifies horizontal and the second value vertical justification. Besides the mentioned values, also numeric values between 0 and 1 can be used. 0 means left justification for the first value and bottom justification for the second value. Note that in view mode, only one value is used.- dots.icon.scale
scaling number that determines how large the icons (or grobs) are in plot mode in comparison to proportional symbols (such as bubbles). In view mode, the size is determined by the icon specification (see
tmap_icons) or, if grobs are specified bygrob.widthandgrob.height- dots.grob.dim
vector of four values that determine how grob objects (see details) are shown in view mode. The first and second value are the width and height of the displayed icon. The third and fourth value are the width and height of the rendered png image that is used for the icon. Generally, the third and fourth value should be large enough to render a ggplot2 graphic successfully. Only needed for the view mode.
- icon.scale
scaling number that determines how large the icons (or grobs) are in plot mode in comparison to proportional symbols (such as bubbles). For view mode, use the argument
grob.dim- grob.dim
vector of four values that determine how grob objects (see details) are shown in view mode. The first and second value are the width and height of the displayed icon. The third and fourth value are the width and height of the rendered png image that is used for the icon. Generally, the third and fourth value should be large enough to render a ggplot2 graphic successfully. Only needed for the view mode.
Details
A symbol shape specification is one of the following three options.
A numeric value that specifies the plotting character of the symbol. See parameter
pchofpointsand the last example to create a plot with all options. Note that this is not supported for the"view" mode.A
grobobject, which can be a ggplot2 plot object created withggplotGrob. To specify multiple shapes, a list of grob objects is required. Tip: for proportional symbols, such as donuts or pies, see the extension package tmap.glyphs.An icon specification, which can be created with
tmap_icons.
To specify multiple shapes (needed for the shapes argument), a vector or list of these shape specification is required. The shape specification options can also be mixed. For the shapes argument, it is possible to use a named vector or list, where the names correspond to the value of the variable specified by the shape argument.
For small multiples, a list of these shape specification(s) should be provided.
Examples
########################
## plot symbol shapes
########################
# create grid of 25 points in the Atlantic
atlantic_grid = cbind(expand.grid(x = -51:-47, y = 20:24), id = seq_len(25))
x = sf::st_as_sf(atlantic_grid, coords = c("x", "y"), crs = 4326)
tm_shape(x, bbox = tmaptools::bb(x, ext = 1.2)) +
tm_symbols(shape = "id",
size = 2,
lwd = 2,
fill = "orange",
col = "black",
shape.scale = tm_scale_asis()) +
tm_text("id", ymod = -2)